Physical Gold vs Paper Gold
Are you considering investing in gold but unsure whether to choose physical gold or paper gold?
The pros and cons of owning physical gold vs paper gold revolve around the liquidity, taxation, tangible access, costs and fees, and degrees of counterparty risk associated with the specific type of ownership. To better understand the subject, we will break down the following:
-
- What is gold,
- What is physical gold,
- What is paper gold,
- What are the differences between physical gold and paper gold.
This article will break down the differences between the two, covering aspects such as acquisition, advantages, disadvantages, and key factors to consider when deciding.
From tangibility and ownership to costs and taxation, we will explore all the important aspects of both gold investments.
So, which is better: physical gold or paper gold? Let’s find out!
What Is Gold?
Gold is a precious metal that has been used for centuries as a medium of exchange and a store of value, and it continues to be a popular investment asset in financial markets today due to its unique properties and historical significance, as highlighted by GOBankingRates.
Gold is easy to buy and sell and functions as a form of wealth preservation insurance. Many experienced investors and capital managers have used gold as a means of hedging against risk for themselves as well as the clients they serve.
What Is Physical Gold?
Physical gold refers to actual, tangible gold that can be held in the form of coins, bars, jewelry, and gold bullion, making it a direct way for investors to own the precious metal.
How Is Physical Gold Acquired?
Physical gold can be acquired through various channels, including purchasing from reputable dealers, buying at market prices, or acquiring from central banks.
When considering buying physical gold, it is crucial to deal with trusted dealers who offer authentic products to ensure the purity and quality of the gold. Reputable dealers play a significant role in facilitating transactions and providing expert advice on investment options.
Some investors opt to store their physical gold with custodians to safeguard their precious metals securely.
Market prices of gold fluctuate based on global demand and economic conditions, influencing the buying and selling decisions of investors. Therefore, staying informed about the current market prices is essential for making informed investment choices.
What Are the Advantages of Physical Gold?
One of the primary advantages of physical gold is that it is a tangible asset that retains intrinsic value and can be stored securely, offering direct ownership without counterparty risk.
Physical gold, unlike paper investments, is a physical commodity that you can hold in your hand, making it a preferred choice for investors seeking a sense of security. Its inherent value comes from its scarcity and universal acceptance as a store of wealth.
When you own physical gold, you have the peace of mind knowing that you have a tangible asset that is not dependent on the stability of financial institutions. This direct ownership gives you control over your investment, enabling you to store it in a way that aligns with your preferences.
Storage solutions for physical gold range from personal safes to secure vaults offered by reputable custodians. These options ensure that your gold remains protected and accessible whenever needed, minimizing the risks associated with storing valuable assets at home.
In today’s uncertain economic climate, where digital currencies and paper assets face volatility, the security of holding physical gold provides a comforting sense of stability and a hedge against inflation. It acts as a timeless symbol of wealth that transcends borders and retains its value over generations.
What Are the Disadvantages of Physical Gold?
Despite its benefits, physical gold comes with certain disadvantages, such as storage risks, insurance requirements, and associated fees.
Storing physical gold in the form of bars or coins can pose security risks, as it might attract theft or could get lost or damaged. Therefore, insuring your gold holdings becomes crucial to safeguard your investment against any unforeseen events.
The process of purchasing gold involves various fees such as premiums over the spot price, shipping charges, and potential transaction or storage fees if dealing with a third-party custodian. Selling gold may incur similar costs and logistical challenges, especially if opting for physical delivery or storage options.
To address these cost concerns, gold IRAs provide a tax-advantaged means of owning physical gold with companies that can provide competitive and occasional waivers of fees, storage, and reasonable buyback policies.
To learn more about how gold investing can protect your long-term wealth and the advantages of tax-deferred gold IRAs, click the banner below to access and download Augusta Precious Metals’ gold IRA checklist to make sure you are aware of all aspects of the gold IRA process:
What Is Paper Gold?
Paper gold refers to investment vehicles such as mutual funds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and shares in gold mining companies, like GLD, that provide exposure to gold without the need to physically own the metal.
How Is Paper Gold Acquired?
Paper gold can be acquired through financial markets, using trading platforms where investors can buy shares of gold ETFs or mutual funds managed by portfolio managers, often detailed in a prospectus.
When investors opt for paper gold, they essentially purchase shares that represent a specific amount of physical gold, providing them with exposure to the precious metal without requiring direct ownership.
This method appeals to those seeking convenience and liquidity in their investments. Portfolio managers play a crucial role in managing these funds, making decisions about buying and selling gold assets based on market conditions and trends.
Investors need to review the fund’s prospectus thoroughly before investing, as it outlines important details such as fees, risks, and investment objectives.
What Are the Advantages of Paper Gold?
One of the key advantages of paper gold is its high liquidity and ease of trading, which allows for seamless integration into a diversified portfolio, as supported by financial institutions like J.P. Morgan.
Investors often appreciate the flexibility that paper gold offers, enabling them to capitalize on market movements without the constraints of physical gold ownership.
The ability to trade paper gold swiftly on major exchanges enhances its appeal as a dynamic investment tool. Due to its liquidity, paper gold can be easily converted into cash when needed, providing a level of financial agility that physical gold may lack.
What Are the Disadvantages of Paper Gold?
Paper gold investments come with specific disadvantages, including counterparty risk, various fees, and susceptibility to market manipulation.
One of the major risks associated with paper gold investments is the potential for counterparty default.
This occurs when the entity backing the investment fails to fulfill their obligations, leading to losses for the investor. Managing these investments often involves fees such as storage costs, management fees, and transaction fees, which can eat into the overall returns. Market manipulation can impact the prices of paper gold, distorting the true value of the investment and possibly leading to losses for investors.
Also, a common feature of paper gold investment products, such as unallocated gold forwards or futures contracts, is the lack of physical gold backing the contract.
There are also third-party modifications and built-in ‘escape clauses’ that can further complicate investment, which increases the counterparty risk. That is why it is incumbent on every investor thoroughly review the contract before moving forward.
What Are the Differences Between Physical Gold and Paper Gold?
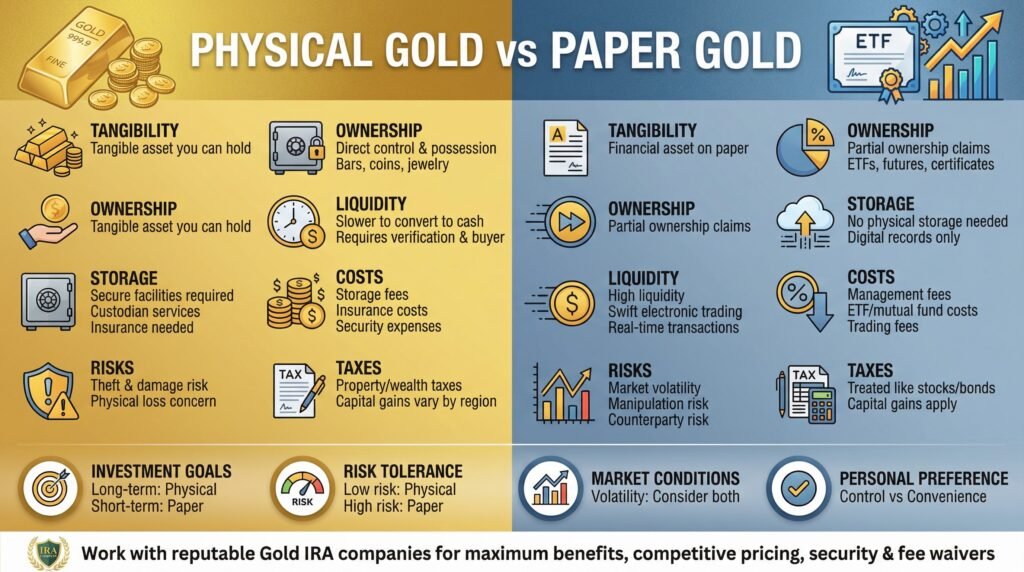
The differences between physical gold and paper gold are significant and multifaceted, encompassing aspects such as tangibility, ownership, liquidity, storage requirements, and associated risks, making each type of gold investment unique in its own way.
Tangibility
Physical gold is a tangible asset that you can hold in your hand, whereas paper gold represents a financial asset that exists on paper.
Investors often find comfort in owning physical gold due to its intrinsic value and the security it provides in times of economic uncertainty. Unlike paper gold, which is subject to counterparty risks and market fluctuations, physical gold serves as a reliable store of wealth that has stood the test of time.
Tangibility plays a crucial role in the psychological aspect of investing; holding a physical asset can instill a sense of ownership and control that paper assets may lack. This physical form also allows for greater flexibility, enabling investors to trade, gift, or display their gold as they see fit.
Ownership
Ownership of physical gold means you have direct control and possession of the asset, while paper gold represents partial ownership or claims on financial assets tied to gold.
Physical gold ownership typically involves owning gold bars, coins, or jewelry that you physically hold or store in a secure location. This tangible form of ownership allows you to directly access and utilize the gold as you see fit.
On the other hand, paper gold ownership often involves holding shares in gold exchange-traded funds (ETFs), gold futures contracts, or gold certificates. While paper gold offers convenience and liquidity, it lacks the intrinsic value and security of physical gold.
Investors often choose between the two based on their investment goals, risk tolerance, and preferred level of control.
Liquidity
Paper gold typically offers higher liquidity due to its ease of trading on financial markets, whereas physical gold might take longer to sell and convert into cash.
Regarding paper gold, transactions can be executed swiftly through electronic platforms, making it highly accessible for investors looking to capitalize on price movements in real-time.
On the other hand, the sale of physical gold involves additional steps such as verifying authenticity, security considerations, and potentially finding a buyer willing to pay fair market value.
This disparity in liquidity stems from the fact that paper gold represents ownership of gold without the need for physical delivery, resulting in a more efficient trading process compared to physically possessing the precious metal.
Storage and Security
Storing physical gold requires secure facilities and often involves custodian services and insurance, while paper gold does not have these storage concerns.
Physical gold, being a tangible asset, necessitates safeguarding measures to protect its physical form. This involves storing it in secure vaults or safes to prevent theft or damage.
Many individuals opt for custodian services where reputable third-party institutions manage and safeguard their gold holdings. Insurance is also crucial as it provides financial protection in case of unforeseen events such as theft, natural disasters, or accidents.
Costs and Fees
Physical gold incurs costs related to storage, insurance, and security, whereas paper gold involves management fees for mutual funds and ETFs.
Regarding physical gold, investors need to consider the expenses of storing their precious metal in a secure facility, wherein storage fees can vary based on the amount and location.
Insurance costs are also a crucial factor in safeguarding against theft or damage. Security measures such as alarms and safes are imperative for protecting the physical gold holdings.
On the other hand, paper gold investors face management fees charged by mutual funds and ETFs, which can eat into their overall returns. These fees typically cover the administrative costs of managing the funds and can vary depending on the provider. There may be trading costs associated with buying and selling paper gold assets.
Risk and Volatility
Both physical and paper gold come with inherent risks; physical gold is subject to theft and damage, while paper gold is more vulnerable to market volatility and manipulation.
Regarding physical gold, the risk of theft is a significant concern for many investors. Storing precious metals at home can make them a target for thieves, and even when stored in secure facilities, there is always a possibility of theft. Physical gold can be damaged or lost due to unforeseen circumstances, impacting its value.
On the other hand, the risks associated with paper gold often revolve around market manipulation. Due to the nature of paper gold being traded on exchanges and through financial instruments, it is more susceptible to price manipulation by large market players.
This can lead to sudden and drastic changes in the value of paper gold, making it a more volatile investment option.
Taxation
Taxation on physical gold and paper gold can vary significantly, with different rules applying to capital gains and financial assets.
Regarding physical gold, the tax implications often revolve around the actual possession of the metal. In many jurisdictions, owning gold bars or coins may be subject to wealth or property taxes.
On the other hand, investing in paper gold, such as gold exchange-traded funds (ETFs) or gold certificates, might be more advantageous from a tax perspective as they are often treated similarly to stocks or bonds.
Transactions involving paper gold can trigger capital gains tax, similar to selling stocks or mutual funds. However, investors should always check with local tax regulations governing these investments, as tax laws can differ significantly across regions and countries.
Which Is Better: Physical Gold or Paper Gold?
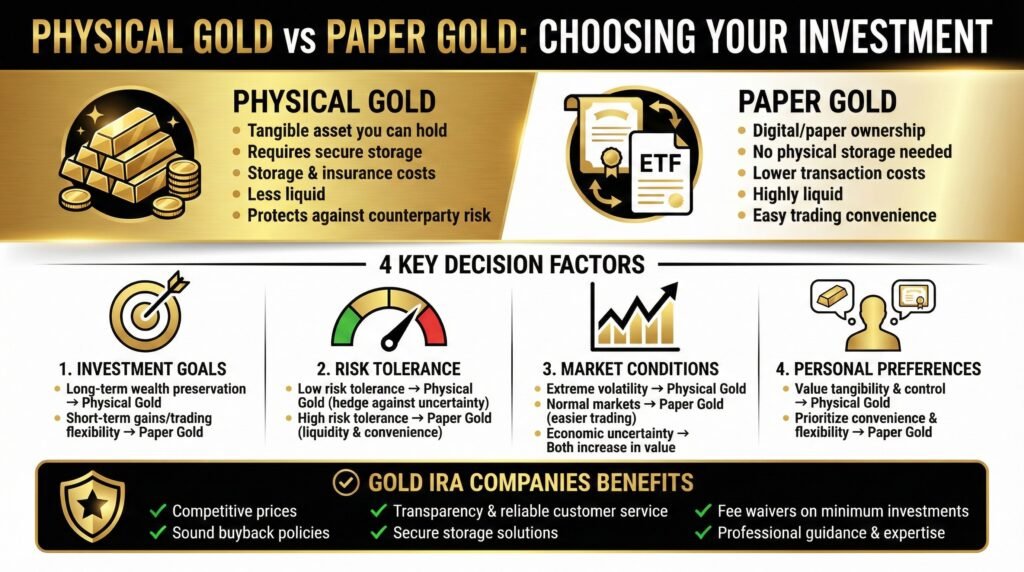
Deciding between physical gold and paper gold depends on various factors, each having its own set of pros and cons that align with different investment strategies and goals.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Physical Gold and Paper Gold
When choosing between physical gold and paper gold, it is crucial to consider several factors, such as your overall investment strategy, the role of gold in your portfolio, and the need for diversification.
One of the key factors to evaluate is your investment timeline. Physical gold, in the form of bars or coins, may require secure storage facilities and can be less liquid compared to paper gold investments like ETFs or futures contracts.
Another factor to weigh is the level of risk tolerance you possess. Physical gold ownership involves unique risks such as theft or loss, while paper gold offers more convenience and ease of trading.
The cost considerations differ between the two. Holding physical gold incurs storage and insurance costs that can erode returns, whereas paper gold investments usually involve lower transaction costs.
Investment Goals
Your investment goals will significantly influence whether physical or paper gold is a better addition to your portfolio.
For long-term wealth preservation, physical gold tends to be a more reliable option, as it has intrinsic value and serves as a hedge against economic uncertainties.
On the other hand, if your focus is on short-term gains or trading flexibility, paper gold instruments like ETFs or futures contracts may be more suitable due to their liquidity and ease of transaction.
Understanding your desired outcome and risk tolerance is crucial in determining the most appropriate form of gold investment. Ultimately, the choice between physical and paper gold depends on your financial objectives and investment strategy.
Risk Tolerance
Risk tolerance is a critical factor in deciding between physical and paper gold, given their varying volatility and associated risks.
Investors with high-risk tolerance levels often lean towards paper gold as it provides convenience and liquidity compared to physically holding gold, which may require storage and insurance costs.
On the other hand, those with a lower risk tolerance may prefer the tangible asset of physical gold as a hedge against economic uncertainties, despite potential costs and limitations in selling quickly.
Market Conditions
Current market conditions can heavily influence the decision to invest in physical or paper gold, as each type responds differently to financial market trends.
For instance, during times of economic uncertainty, investors often flock to gold as a safe-haven asset, driving up the prices of both physical and paper gold.
Physical gold may hold an advantage in times of extreme market volatility, as it is a tangible asset that you can possess physically, reducing counterparty risk. On the other hand, paper gold, such as exchange-traded funds (ETFs) or gold futures, offers greater liquidity and convenience for trading.
Personal Preferences
Personal preferences play a significant role in the choice between physical and paper gold, especially regarding the form of ownership and control desired.
For individuals who value the tangibility and security of physical assets, holding actual gold bars or coins might be more appealing as they can physically see and touch their investment.
On the other hand, those who prioritize convenience and ease of trading might opt for paper gold, such as gold ETFs, which offer flexibility and liquidity without the need for physical storage.
Take, for instance, a seasoned investor who prefers the flexibility to quickly buy or sell portions of their gold holdings. For this investor, paper gold provides a more dynamic and easily accessible option.
Working with a Reputable Gold Investment Company for Physical Ownership
When embarking on the path of gold investing, working with a trusted and reputable gold investment company can alleviate a great deal of the guesswork, time, and possible financial setbacks.
Leveraging the institutional knowledge of these companies will provide you with the ability to maximize your gold investment.
Gold IRA companies, more specifically, can provide additional benefits beyond merely buying physical gold from a local dealer. These companies offer competitive prices, sound buyback policies, transparency, reliable customer service, and robust security of your precious metals.
This option alleviates the worry of holding and securing the gold within your own home. Dependent on the volume of physical gold you intend to own, it is usually advised that you do not put all your wealth in one place. Also, many gold IRA companies will waive certain fees depending on the investment minimum.
Finding the right gold IRA will also depend on whether you are a high-net investor looking for the most competitive prices or require a lower investment minimum and affordable entry to the gold market, we have researched and reviewed our best 4 gold IRA and precious metal investment companies that meet those individual needs whether you prefer a gold IRA or owning the physical gold in your place of residence. See our gold IRA reviews for more information so you can make the right choice.
Furthermore, if you have 100k in savings to protect and want to take advantage of the best gold prices and lifetime customer support, attend a free gold and silver educational web conference hosted by Augusta Precious Metals. Secure your place today by clicking the banner below.
Tap the banners below to go to the official gold company site and find the right option for you.
In light of the inherent risks associated with paper gold investments, you must understand the implications of the impending decline of the dollar as the global reserve currency.
The dollar’s fall is inevitable due to several factors. Let’s delve into the reasons behind this and why gold becomes a strategic investment in this scenario.
-
- Quantitative Easing Policies: The U.S. Federal Reserve’s approach to pump money into the economy, known as Quantitative Easing, has led to an overabundance of dollars. This excess supply inevitably devalues the dollar, weakening its position as the global reserve currency.
- Central Banks’ Actions: Countries with sizeable monetary reserves, generally held in dollars, are increasingly converting their reserves into tangible assets like gold. Nations like Russia, China, and Brazil are leading this trend, seeking to preserve the purchasing power of their reserves. This move away from the dollar is accelerating its devaluation.
- Lack of Viable Alternatives: Other international currencies don’t offer a compelling alternative as they’re all based on unconvertible paper. The lack of a strong alternative to the dollar accelerates the process of ‘de-dollarization’, leading to increased demand for gold.
As the decline of the dollar seems inevitable, investing in gold becomes a strategic move. Gold, as a tangible asset, stands to gain significantly from the dollar’s fall.
It offers a reliable store of value and acts as a hedge against currency devaluation. So, not only does gold provide a safeguard against the falling dollar, but it also presents potential capital appreciation opportunities.
Conclusion
To conclude, you are now aware of the various advantages and disadvantages of owning physical gold vs paper gold investment products. Weighing the tangible benefits of physical gold ownership vs the convenience of paper gold contracts, which involve greater counterparty exposure, can inform one’s investment preference.
What you decide will be based on your own specific needs. Best of luck on your gold investing journey.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between physical gold and paper gold?
Physical gold refers to physical bars or coins made of gold, while paper gold refers to gold held in the form of certificates or contracts.
Which is a better investment, physical gold or paper gold?
It ultimately depends on your investment goals and risk tolerance. Physical gold provides tangible ownership and can be easily liquidated, while paper gold offers convenience and lower transaction costs.
Is physical gold more secure than paper gold?
Physical gold is considered to be more secure as you have direct ownership and control over it. Paper gold, on the other hand, relies on the stability and credibility of the issuing institution.
Can I convert my physical gold into paper gold?
Yes, you can convert your physical gold into paper gold through various methods such as ETFs, futures contracts, and gold-backed investment accounts.
What are the disadvantages of owning physical gold?
The main disadvantage of physical gold is the cost and inconvenience of storing and insuring it. It may also be subject to higher transaction costs and potential for theft.
Are there any risks associated with paper gold?
Yes, there are risks associated with paper gold, such as counterparty risk, market volatility, and potential for fraud or default by the issuing institution.
Find the right gold IRA conpany for you. Obtain a gold IRA guide and talk to a broker




If you have 100k in savings to protect, attend a gold investment educational webinar hosted by Augusta Precious Metals. Tap the button below:
Gold IRA FAQs

Adam ONeill
Author, lifelong investor, and creator of PreciousMetalsInvestmentPortfolio.com


